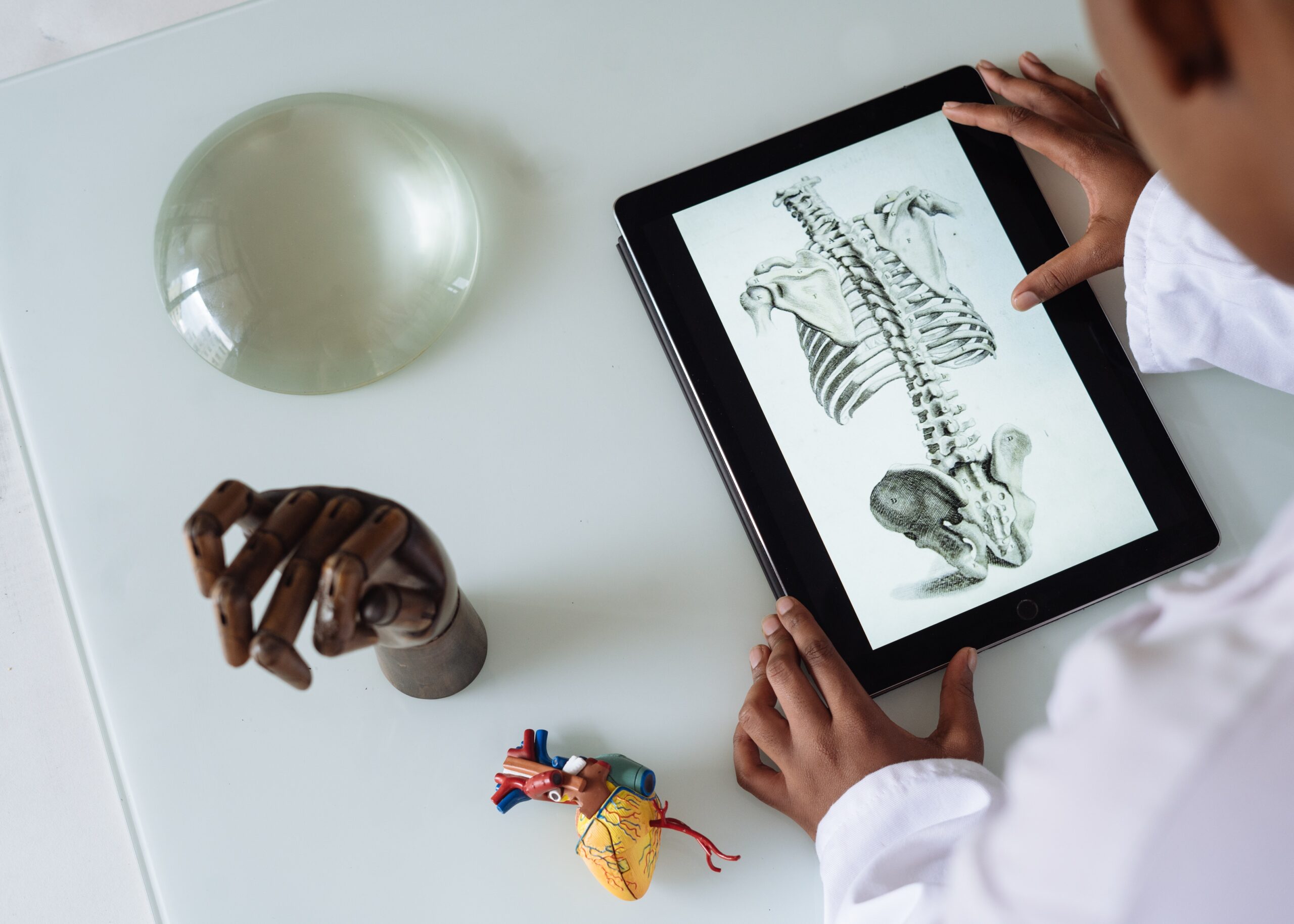
The Significance of Studying Anatomy
The study of anatomy, the science that investigates the physical structure of organisms, holds a position of vital importance in the broad field of biological sciences, specifically in medicine and healthcare. Its significance lies in its fundamental role of facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the physical organization and function of living organisms, particularly the human body.
One of the key benefits of studying anatomy is the understanding it imparts about the structure-function relationship in organisms. Every part of the body, be it minute like cells and tissues, or larger structures like organs, organ systems, and the organism itself, has a specialized role to play. Understanding these relationships is critical to comprehend the remarkable machinery of life. For example, knowing the structure of the heart helps us understand how it pumps blood throughout the body, while knowledge of skeletal anatomy aids in understanding body movements.
In the healthcare sector, the significance of anatomy cannot be
overstated. A detailed knowledge of human anatomy is fundamental to the
practice of medicine. From diagnosis to treatment and surgery, a
clinician's proficiency is based on their understanding of the patient’s
anatomy. In complex medical procedures such as surgeries, detailed
anatomical knowledge guides the surgeon's hand, reducing the risk of
unintended damage to vital structures and enhancing the precision and
safety of interventions.
Moreover, understanding anatomy is also
crucial for interpreting medical imaging like X-rays, CT scans, and
MRIs. These imaging techniques provide a visual representation of the
internal structure of a patient's body, and interpreting them accurately
requires a deep understanding of anatomy. Hence, radiologists,
surgeons, and other clinicians are often well-versed in the intricacies
of anatomy.
Furthermore, knowledge of anatomy is instrumental in
understanding the development and progression of diseases. An anatomical
viewpoint provides insights into how structural abnormalities or
injuries can lead to physiological dysfunction, paving the way for
pathological conditions. For example, understanding the anatomy of the
respiratory system helps to understand conditions like asthma or COPD,
where structural changes in the airways can lead to impaired gas
exchange.
Studying anatomy also has a significant impact on the
development and improvement of medical technology. Prosthetics, surgical
robotics, medical imaging technology, and more are all areas where
understanding anatomy can lead to innovations. For example, the design
of prosthetic limbs requires a detailed knowledge of the skeletal and
muscular system to ensure proper fit and function. Similarly, the
development of surgical robots necessitates a comprehensive
understanding of the surgical field, which is fundamentally an
anatomical concept.
In a broader perspective, the study of anatomy can contribute to fields
beyond medicine. From informing the creation of more realistic
animations in the film industry to helping athletes understand their
bodies and optimize their performance, the applications of anatomy are
wide and varied.
In conclusion, the significance of studying
anatomy lies in its direct contribution to the understanding of life
itself. It equips us with critical insights into the organization and
functioning of the body, thereby aiding in diagnosis and treatment of
diseases, guiding surgical interventions, enhancing medical technology,
and even finding applications in diverse fields outside medicine. The
study of anatomy, thus, stands as a cornerstone of biological sciences.
Basic Concepts in Anatomy
To commence your anatomy studies with help of anatomy study guide, let's discuss the fundamental concepts:
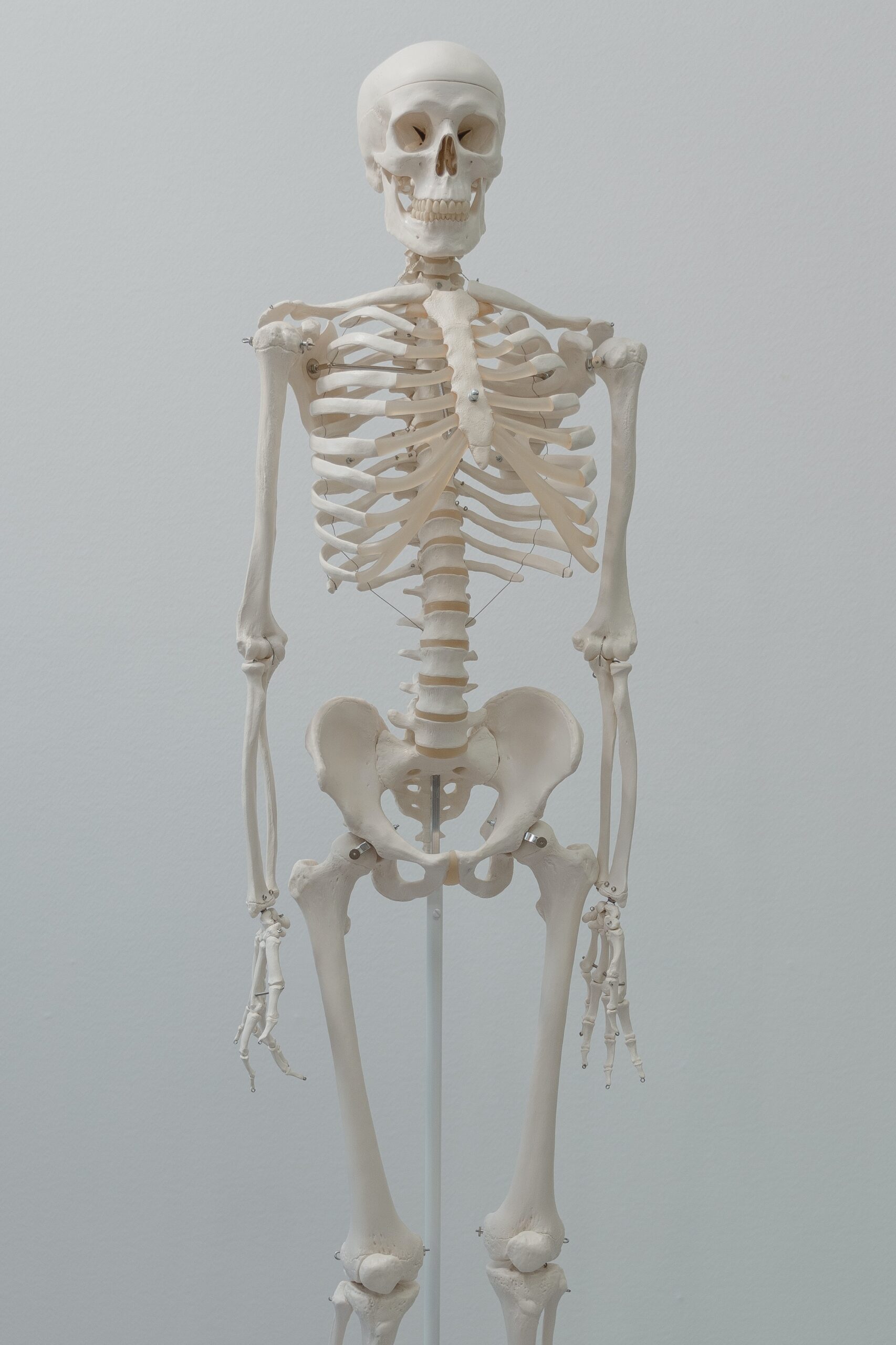
Systematic Study of the Human Body
According anatomy guide this section delves into the major systems of the human body:
Musculoskeletal System: Comprising bones, muscles, and joints, this system provides support, movement, and protection.
Cardiovascular System: Includes the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It transports nutrients, hormones, and gases throughout the body.
Nervous System: Comprises the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It controls and coordinates body functions.
Respiratory System: Involves the nose, trachea, lungs, and other structures involved in breathing.
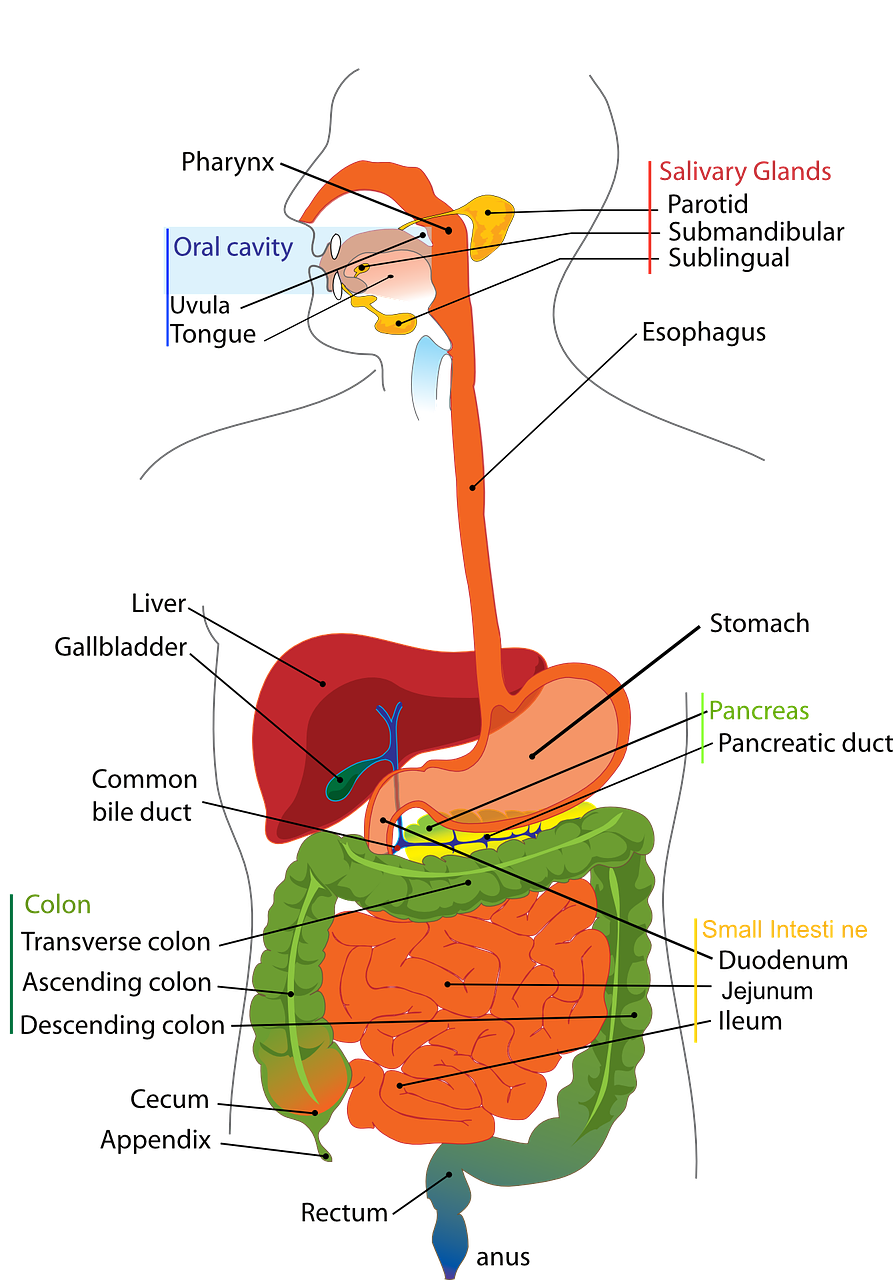
Digestive System: Begins at the mouth and ends at the anus, including the stomach and intestines. It processes food for energy and rids the body of waste.
Endocrine System: Encompasses hormone-producing glands like the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands. It regulates body functions such as growth and metabolism.
Urinary System: Includes kidneys, bladder, and associated structures. It eliminates waste from the body and regulates fluid balance.
Reproductive System: Responsible for producing offspring. Structures differ in males and females.
Anatomy Tools and Techniques
In the study guide, you can immediately understand exactly what methods and ways of studying the material exist and how the study of this area is carried out.
Dissection, medical imaging, and microscopy are three vital methodologies employed within the field of biological sciences and medicine. Each of these techniques contributes significantly to our understanding of anatomy and the functioning of the body, while also playing pivotal roles in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Dissection
Dissection is a hands-on technique that involves the careful cutting and separating of tissues to reveal their structural relationships. It is one of the most traditional and enduring methods of studying anatomy. Its significance lies in its ability to provide an in-depth, three-dimensional understanding of the body's structures, which is critical for medical students and researchers alike. Additionally, through the dissection of cadavers, students learn not only about normal anatomy, but also pathological conditions and variations, which can differ significantly among individuals. Therefore, dissection serves as a foundation for developing a comprehensive understanding of the human body, aiding in refining surgical skills, and advancing anatomical research.
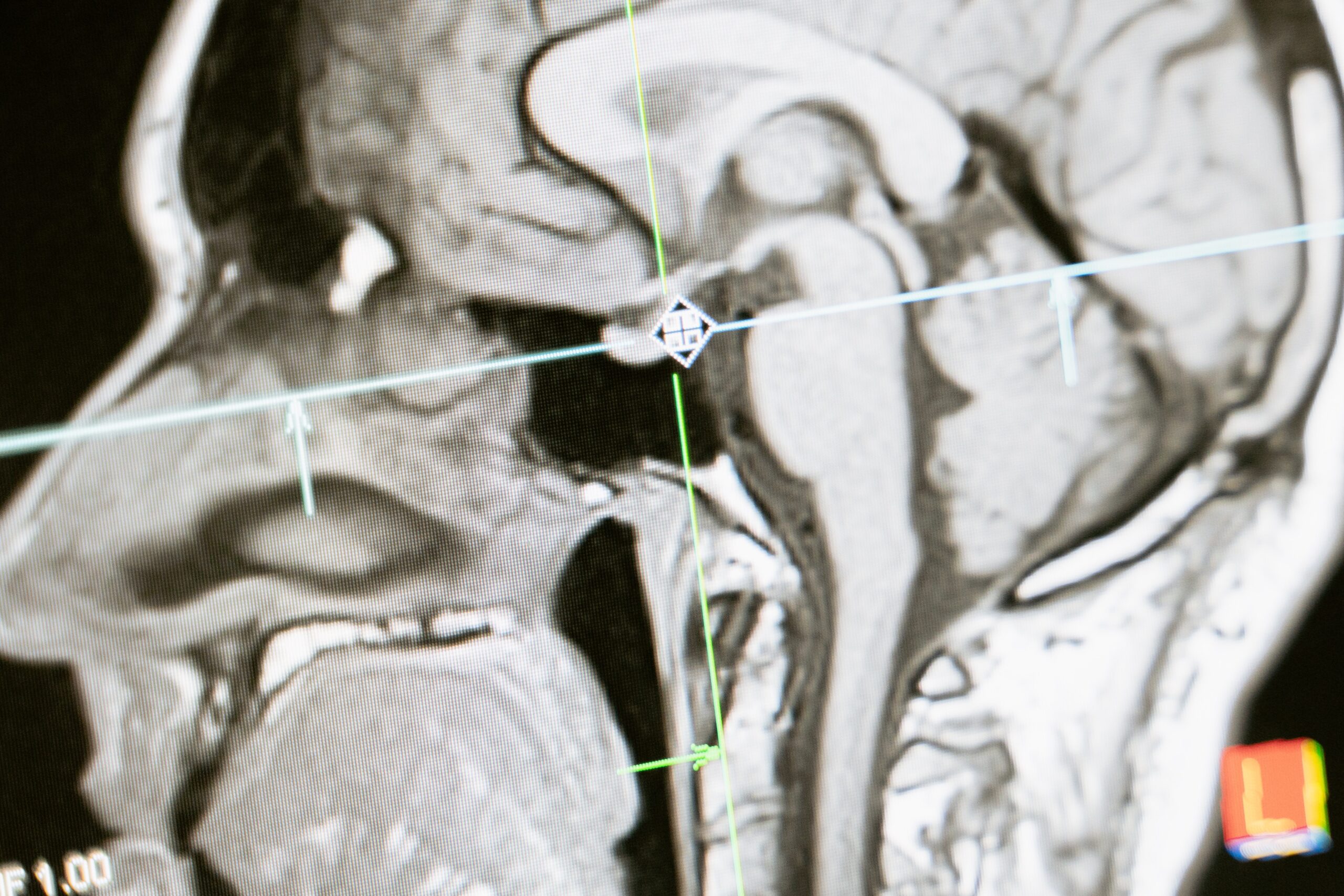
Medical imaging
Medical imaging, including Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computed Tomography (CT) scans, and ultrasound, provides non-invasive ways to visualize the body's internal structures. MRI and CT scans allow for detailed cross-sectional images of the body, offering insights into the body's deep structures without the need for invasive procedures. These technologies are invaluable in diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of health conditions, from cancer to cardiovascular disease. Ultrasound imaging, on the other hand, uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of the body's internal structures, including organs and vessels, and is instrumental in fields like obstetrics and cardiology.
Microscopy complements
Microscopy complements these macro-level exploration techniques by providing a micro-level perspective of the body's structures. Microscopic examination allows for the viewing of cells and tissues at a magnified scale, which is fundamental in studying cellular structure and function. From identifying cell types and understanding tissue architecture to diagnosing diseases at a cellular level (like identifying cancer cells), microscopy plays a critical role. Specialized forms of microscopy, such as electron microscopy, can provide even more detailed views, allowing scientists to explore sub-cellular structures like organelles and even molecules.
Together, these methodologies – dissection, medical imaging, and microscopy – provide complementary perspectives and levels of resolution in the study of anatomy and physiology. By integrating macroscopic views with microscopic insights, they enhance our ability to understand the complexity of the human body, support diagnostic processes, guide therapeutic interventions, and fuel advancements in biomedical research.
Studying and Learning Techniques for Anatomy
The journey through an anatomy study guide can be made easier with effective studying and learning techniques. Here, we delve into some approaches that can significantly improve your understanding and retention of anatomical knowledge.

Remember, the key to effectively studying anatomy is consistent review and active engagement with the material. Tailor these techniques to your personal learning style and keep your goal in mind, whether it's passing an exam, entering a medical profession, or simply satisfying a curiosity about the human body. This guide is designed to support your learning journey every step of the way.
Anatomy Quizzes and Exam Preparation
Quiz Questions: Divided by topic, these can help reinforce learning and identify areas that need further study.
Mock Exams: These simulate the experience of an actual exam, aiding in better preparation.
Tips for Exam Preparation: These might include developing a study schedule, taking breaks, and eating healthily.
Answer Keys and Explanations: These not only provide the correct answers but also explain why they're correct, enhancing understanding.
This anatomy study guide is designed with user-friendly navigation tools like a search bar, site map, and breadcrumbs to ensure an efficient and seamless study experience. Dive in, explore, and enjoy the journey to mastering anatomy.